The Effect of Rising Higher Education Costs on Business Formation
The Effect of Rising Higher Education Costs on Business Formation
Authors: Lea Rendell
Abstract: Between 2000 and 2014, yearly real average college tuition increased by 31% while the average student loan balance increased by 21%. I use administrative data to examine how an increase in the cost of higher education affects the likelihood of forming a business after graduation. I instrument for realized tuition by exploiting the variation in total four-year tuition due to differences in the length of exposure to increased tuition between students in different enrollment years at universities that experienced a large “sticker price” tuition shock. I find that for every $10,000 increase in tuition there is a 3.0 percentage point (41 percent) decrease in the likelihood of being an owner or early joiner of a business. This decline is 7.8 percentage points larger for individuals at universities that have larger student loan balances and 4.1 percentage points higher for individuals with parents who did not complete college. The negative effect on business formation does not exist for students attending universities with more generous financial aid. These results suggest that increasing higher education costs are deterring recent graduates from engaging in entrepreneurial activity.
Seminar Notes
Venue
CES Brownbag 2024
Objective
To understand if rising education costs decrease entrepreneurship
Importance
Two reasons higher education costs might decrease entrepreneurship -
Funding constraints - may reduce financial resources needed to start a business or student loans may reduce likelihood of getting funding.
Risk aversion - new businesses are risky. May be less willing to take on risk if in debt (student loans)
Background
Between 2000 and 2014 - 31% increase in average published tuition rates and 21% increase in average student loan balance.
Literature has documented negative long-term effects of student loans on marriage rates, homeownership, job market.
Declining share of young entrepreneurs.
Data & Key Variables
National Survey of College Graduates (NSCG) - institution and background info. 90,000 individuals per survey year 2013, 2015, 2017, 2019, 2021. 1/3-1/2 of respondents are newly sampled each year. 2004-2011 graduates
Tuition data - IPEDS - calculate 4 year tuition bill
Business Formation data - BR & LBD, ILBD, LEHD
Choi et al (2023) method to identify “Founding team”; owner. Employer & non-employer firms.
Measured within 8 years of graduation
Methodology
Use variation in tuition and the timing of tuition shock relative to stage of college education.
Shock = year-over-year change of over $1000
Students further from graduation when shock occurs will have a larger tuition balance
Results
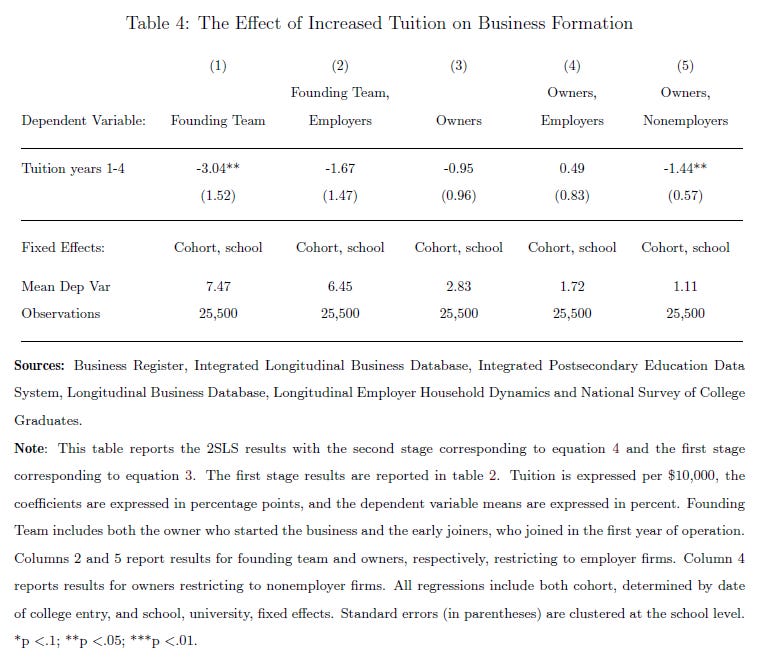
Decrease in entrepreneurship, measured as being part of a founding team, of ~3 percentage points for every $10,000 of tuition. A 40% decrease relative to the mean.
Larger effects at schools with high loan rates, and for students with lower educational background parents